
Its decisions impact everything from query latency to infrastructure efficiency, making it one of the most critical components in modern database performance.
As Head of Product Services for Fujitsu Enterprise Postgres, I’ve seen firsthand how optimizer advancements translate into real-world business outcomes. At the recent PGDU 2025 conference in Sydney, I couldn’t present this session live, but I’ve prepared a comprehensive slide deck that we’re now sharing here for a wider audience.
This isn’t just a retrospective—it’s a practical guide to the innovations shaping PostgreSQL today and how you can leverage them for competitive advantage.
Why this matters
The query optimizer is no longer a simple cost-based planner. It has become a sophisticated engine that:

- Understands data relationships through extended statistics
- Exploits parallelism to harness every CPU core for faster analytics
- Applies smart caching and incremental sorting to minimize wasted cycles
- Adapts dynamically with features like JIT compilation, partition pruning, and memoization
These capabilities deliver tangible benefits: faster queries, predictable performance, and reduced operational overhead—critical for enterprises running mission-critical workloads.
What you'll learn in the presentation
Among others, I explore the topics below:

- The core challenge
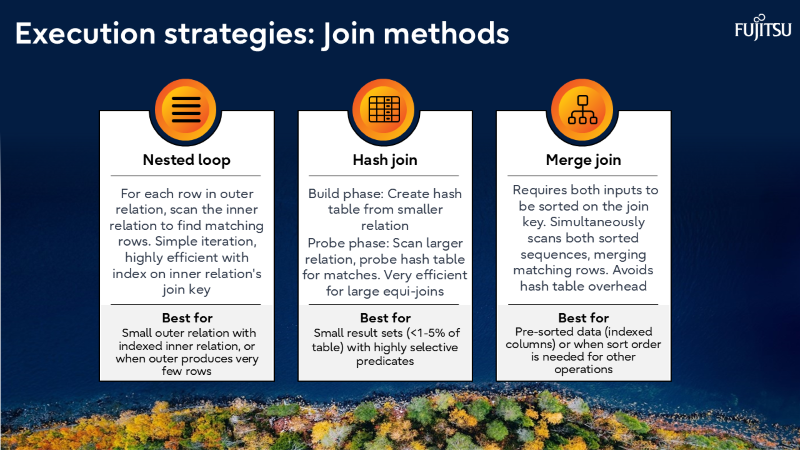
Why join order selection is NP-hard and how PostgreSQL solves it.
- Key milestones
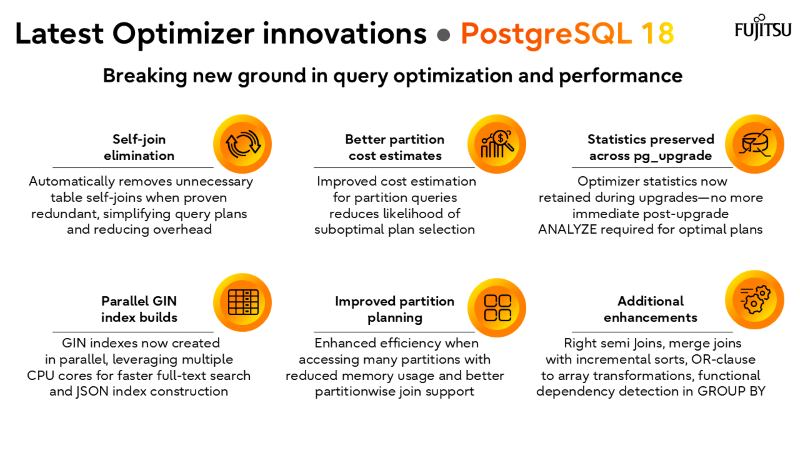
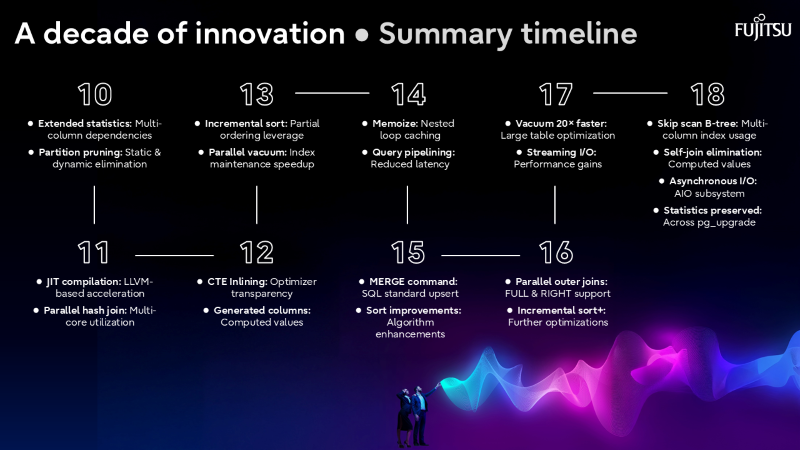
From PostgreSQL 9.6’s first parallel execution to PostgreSQL 18’s self-join elimination and asynchronous I/O.
- Performance features explained
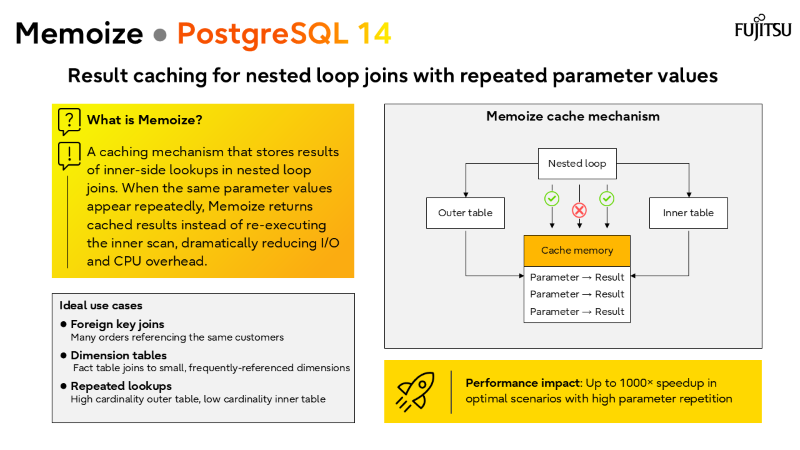
Extended stats, incremental sort, memoize, and parallel GIN index builds.
- Practical insights
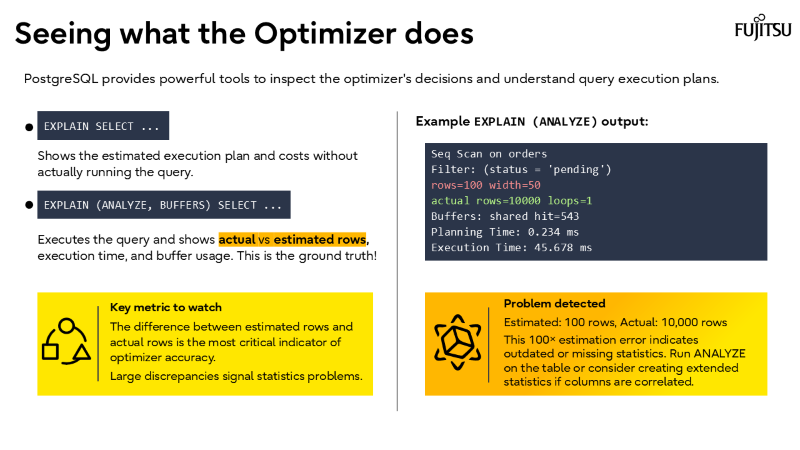
How these features impact query planning and what DBAs and architects should do to take advantage of them.
The strategic impact

The latest release, PostgreSQL 18, exemplifies this philosophy. Features like self-join elimination, statistics preservation across upgrades, and parallel GIN index builds are not just incremental improvements—they represent a shift toward smarter, more autonomous optimization. Combined with asynchronous I/O and refined partition planning, these capabilities ensure that PostgreSQL remains a top choice for enterprises seeking both performance and reliability.
Key takeaways

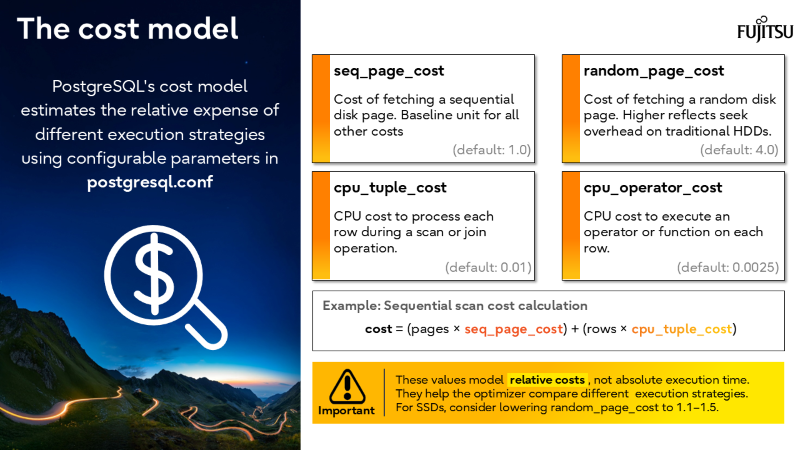
- Optimizer intelligence matters
Every improvement reduces wasted work and accelerates queries.
- Parallelism is now mainstream
From PostgreSQL 9.6 onward, multi-core utilization is a game-changer for analytics.
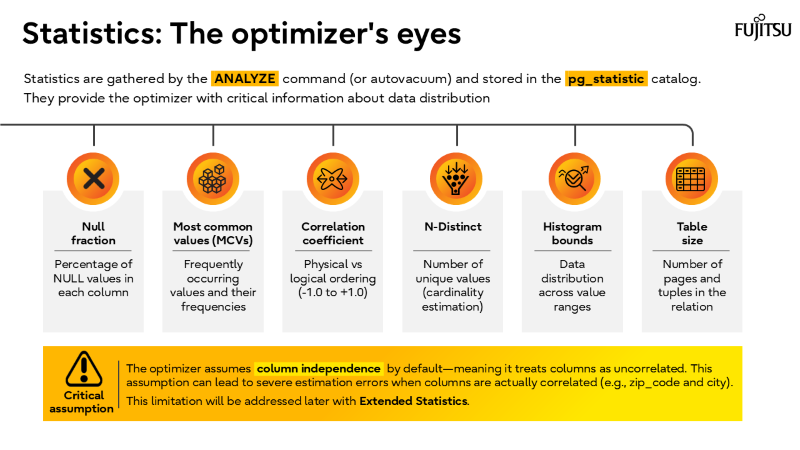
- Statistics are the foundation
Extended statistics and accurate cardinality estimates drive better plans.
- Modern features deliver real gains
Memoize, incremental sort, and JIT compilation can cut execution times dramatically.
- PostgreSQL 18 sets a new benchmark
Self-join elimination, async I/O, and parallel index builds redefine performance at scale.
Explore the full presentation and discover how a decade of innovation in PostgreSQL’s query optimizer can help you unlock new levels of performance.
The evolution of PostgreSQL Query Optimizer A Decade of Innovation (2015-2025) - From single-core OLTP to multi-core analytical powerhouse
 Click to view the slides side by side
Click to view the slides side by side Top to bottomClick to view the slides in vertical orientation
Top to bottomClick to view the slides in vertical orientation

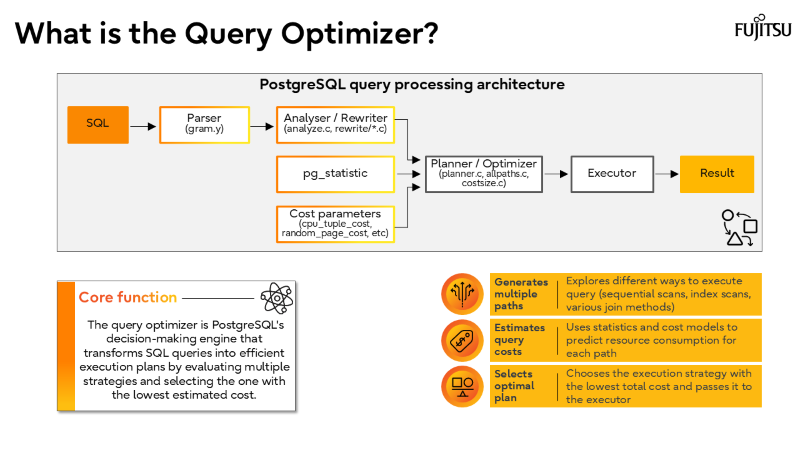
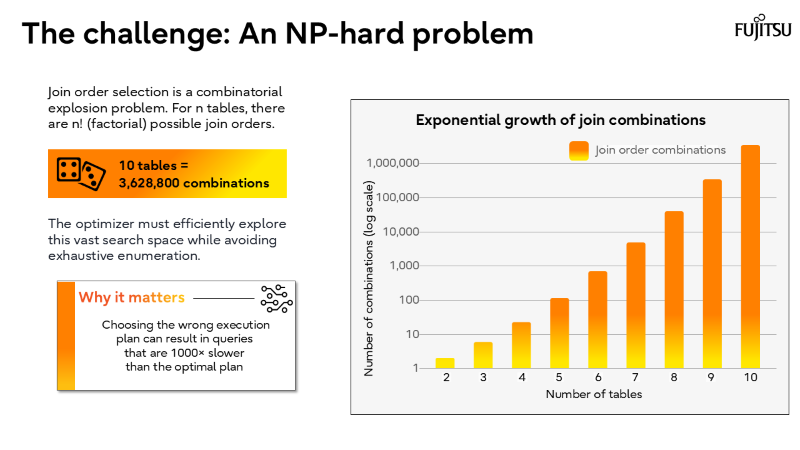
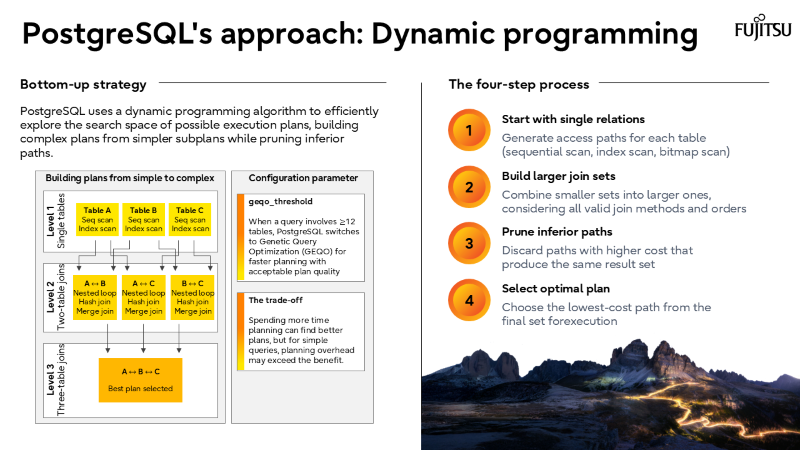
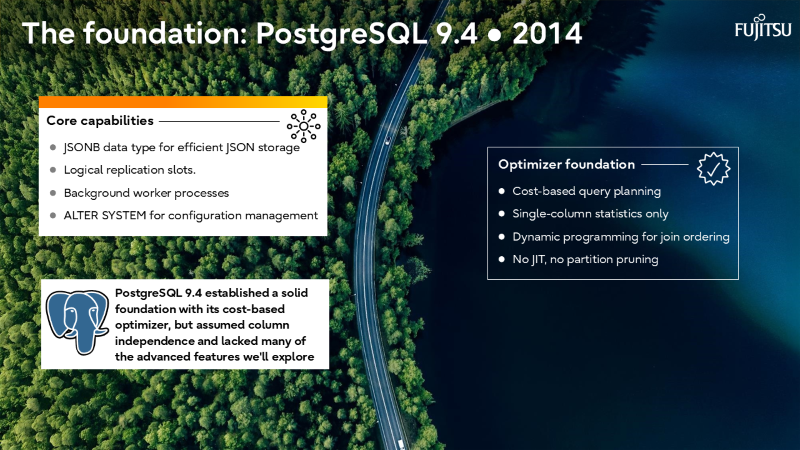

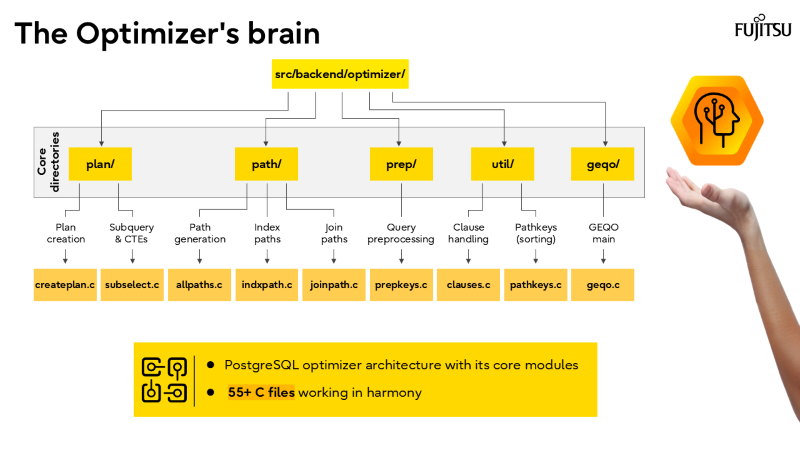
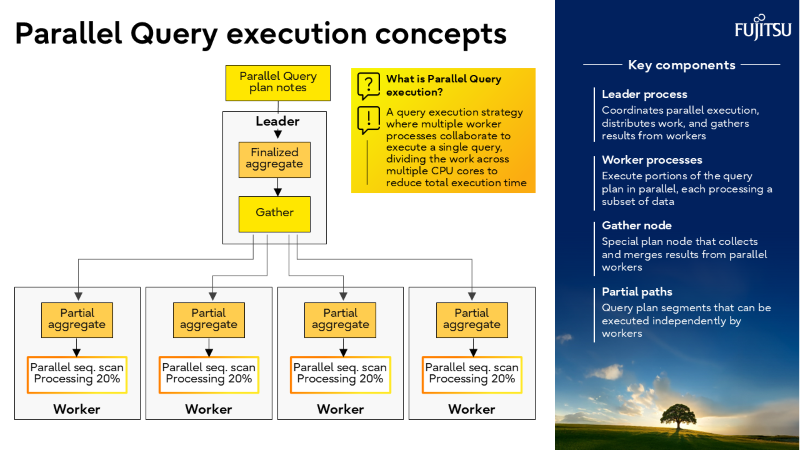
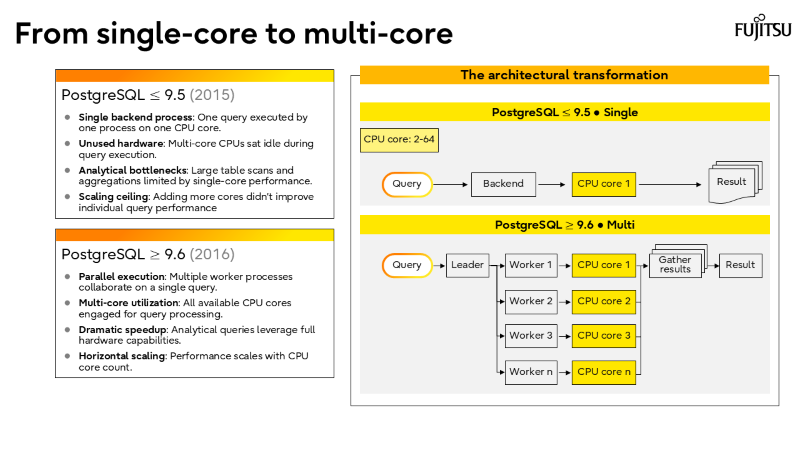

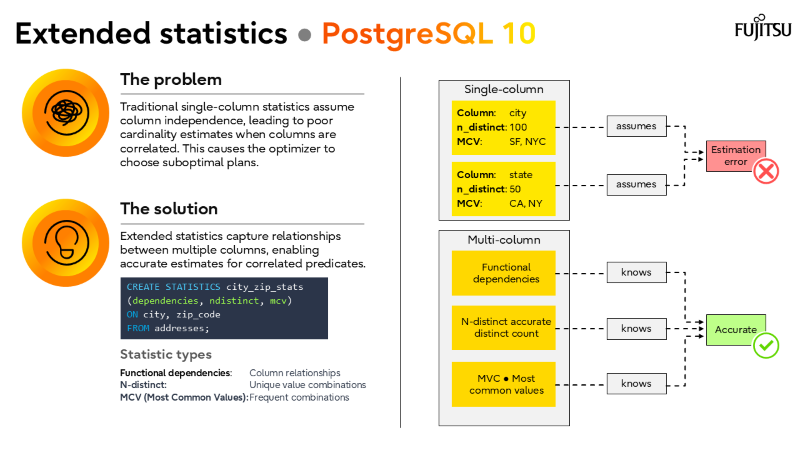
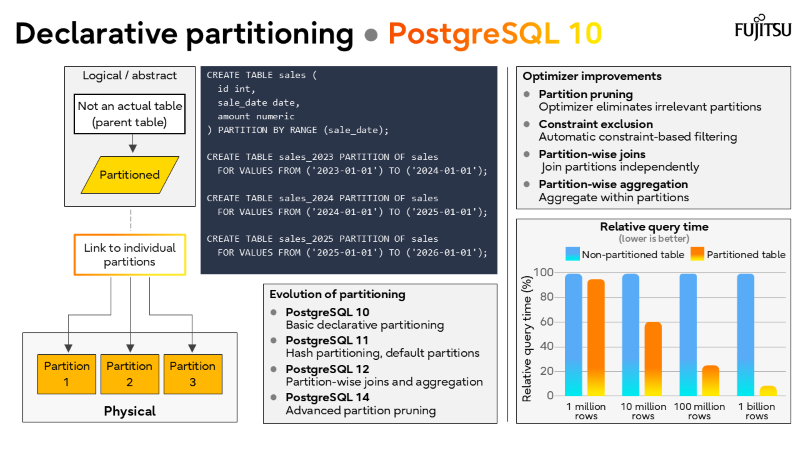
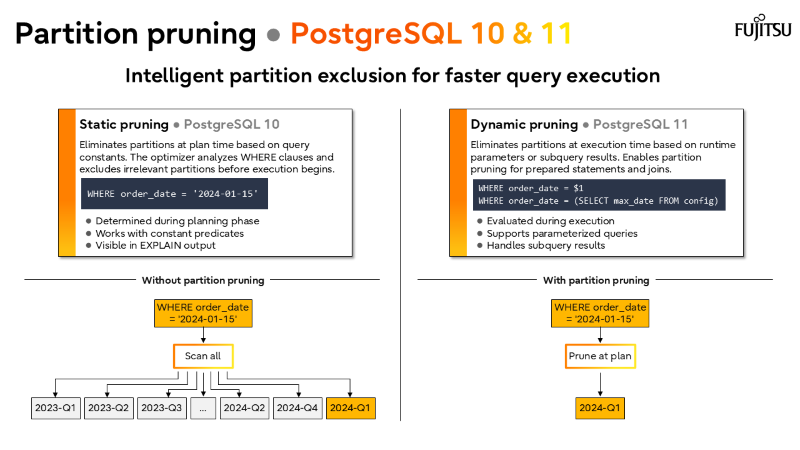
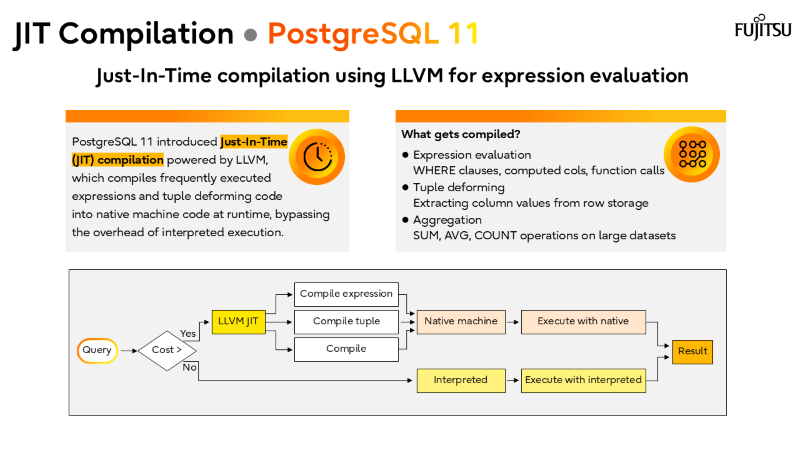
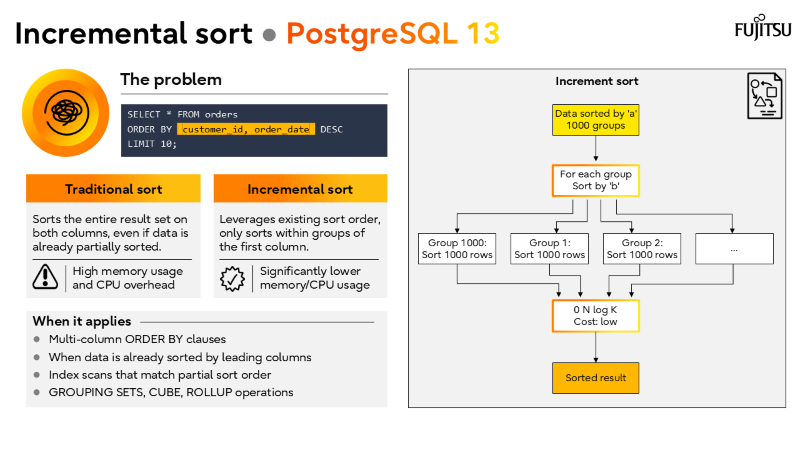


I’ve also recorded a brief walkthrough of the slide deck above, which you can watch in the short video below.
Stay tuned for more insights from Fujitsu Enterprise Postgres on turning these features into production wins.




