Databases store critical customer data, so it is vital to back up regularly in case of database failure. This article explains backup and recovery of PostgreSQL and Fujitsu Enterprise Postgres databases, covering the fundamentals of backup to the benefits of using Fujitsu Enterprise Postgres.
What is PostgreSQL backup/recovery?
First, we will explain the basics of backup. PostgreSQL database backup methods include logical backup and physical backup.
- Logical backup
Extracts the data stored in the database to a file. Obtaining the data in the form of SQL takes a long time, but the flexibility is superior because it allows migration to other versions or other systems.
- Physical backup
Physically copies the database files. The time required to copy files is shorter, so this method is useful for recovery from hardware failures.
Logical backup
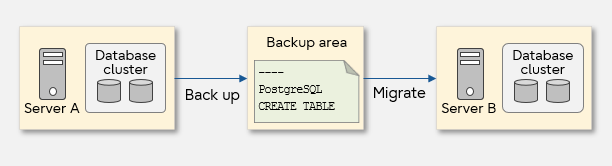
Physical backup
Next, we will explain each backup method in detail.
Logical backup
The logical backup extracts the database data to a file while the PostgreSQL database is running. The following commands are available to perform logical backup.
- pg_dumpall command
Backs up the contents of the entire database cluster in SQL format. You can then run the psql command to restore the database cluster using the latest backup.
- pg_dump command
Backs up the contents of the specified database in SQL format. When using the backup in archive file format, run the pg_restore command to restore the database.
- SQL command COPY
Backs up the data in the specified table in its own text format, binary format, or CSV format. This command also recovers the data to the latest backup point.
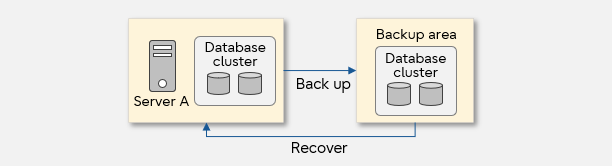
Physical backup
Physical backup is a physical copy of the database files as they are. Depending on the timing of the operation, it can be either an offline backup, if it is acquired while the database is stopped, or an online backup, if it is acquired while the database is still running.
Offline backup
The entire database cluster is backed up by copying all database files using the commands provided with the OS while the PostgreSQL database is stopped. The acquired backup data can be used for restoring the cluster to the backup point by running the command provided with the OS and then starting the PostgreSQL database.
Online backup
Online backup is acquired with the PostgreSQL database still running.
First, take a base backup as a starting point. The data is updated even while the base backup is being acquired, so the update process is saved as a transaction log, or write-ahead log (hereinafter abbreviated as WAL). WAL is archived as needed and stored as an archive log. In case of some failure such as database destruction, use the base backup, archive log, and WAL to recover.
What is WAL / transaction log?
The WAL (write-ahead log) or transaction log is the history of changes made to the database by transactions.
The following shows the flow from acquiring an online backup to recovering to the latest status after a problem occurs.
Online backup flow
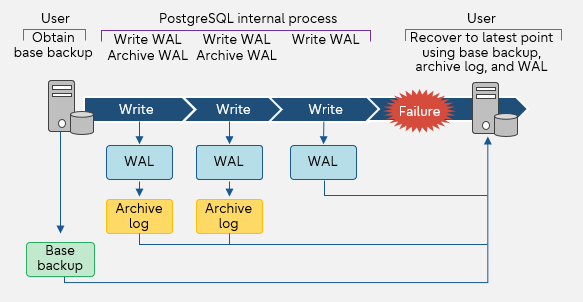
With the recovery using archive log and WAL, it is possible to recover to the backup point, the latest point, or any time.
The online backup features of PostgreSQL are as follows.
- Online backup with continuous archiving
You set the database in backup mode, copy the files using the OS feature, etc., and then end backup mode after the copy is complete. The acquired backup data will be recovered using point-in-time recovery. For the restore point, you can set the backup point, any specific time, or any point.
In addition to the features of PostgreSQL, Enterprise Postgres also provides the following online backup features.
- pgx_dmpall command
A command provided by Enterprise Postgres to perform an online backup by a continuous archive with one touch. The acquired backup data can be recovered using the pgx_rcvall command or WebAdmin. For the restore point, you can set the backup point, any specific time, or any point.
- WebAdmin
A GUI provided by Enterprise Postgres to perform a one-touch online backup with a continuous archive. You can recover to the point when the backup was acquired or the latest time.
Both methods back up the entire database cluster.
What is point-in-time recovery?
It is a feature that specifies an arbitrary time between the backup point and failure and restores the data to the specified time. For example, if a database has been updated incorrectly, you can restore it by specifying the date and time when the backup was complete.
What is the pgx_rcvall command?
It is a command provided by Fujitsu Enterprise Postgres to perform recovery using a backup created by the pgx_dmpall command and the archive WAL. For details on the command, refer to
Fujitsu Enterprise Postgres Reference Guide > Chapter 3 - Server commands > pgx_rcvall
How to decide the backup method
As you can see, there are various ways to back up a PostgreSQL database, so how should you choose a method that suits your business?
The selection criteria must consider factors such as: to what point in time should the data be recovered, whether the service running can be stopped for a backup, and what kind of event is predicted. The following lists some sample requirements with the optimal backup method.
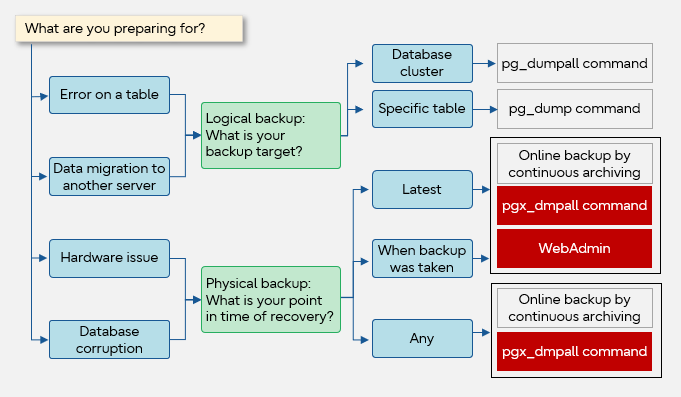
- To recover only one table after its data was lost due to incorrect operation
- Logical backup using the pg_dump command.
- To build a new system on another server, migrate all the data from the old system, and continue operation
- Logical backup using the pg_dumpall command, because the entire system will be migrated.
- To recover data to the latest point just before a disk hardware failure
- Physical backup via online backup by continuous archiving, WebAdmin, or the pgx_dmpall command.
- To recover to the point in time when the data was logically destroyed after detecting that the database is not working properly
- Physical backup via online backup by continuous archiving or the pgx_dmpall command.
The following shows the flow of selecting a backup method that addresses these requirements. The Fujitsu Enterprise Postgres features are indicated with red boxes.
Examples of selecting a backup method
Summary of PostgreSQL backup and recovery
The table below sumarizes the types of backup and recovery available with PostgreSQL and Fujitsu Enterprise Postgres features.
| Type |
Overview |
Backup method |
Backup target |
Restore point of recovery |
| Backup |
Latest |
Any |
| Logical backup |
Data is retrieved and saved while the database is running. It is also possible to back up in units of definition and data. |
pg_dumpall command |
Database cluster |
 |
 |
 |
| pg_dump command |
Database |
 |
 |
 |
| SQL command COPY |
Table |
 |
 |
 |
| Physical backup |
Offline backup |
Physically copy the database files while the database is stopped. |
OS command |
Database cluster |
 |
 |
 |
| Online backup |
Physically copy the database files while the database is running. WAL is also used. |
Online backup with continuous archiving |
Database cluster |
 |
 |
 |
| WebAdmin |
Database cluster |
 |
 |
 |
| pgx_dmpall command |
Database cluster |
 |
 |
 |
Select the optimal database backup method that meets the system operation management requirements, and perform maintenance operation of the business data.












